
Are you using TLS or SSL?
Ok, so let’s start from the beginning, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) was the standard technology to encrypt data over the internet when transmitting sensitive /private data such as your password when shopping online, card/pin or social security number and so on all before the advent of TLS, SSL expired in 1996 with SSL v3 although people still referred to the internet security as SSL till date, wrong nomenclature.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) in simple terms is the advanced version of SSL if I can say that, it encrypts data sent over the Internet to ensure that hackers are not able to see the content of transmitted data especially when transmitting sensitive /private data such as your password when shopping online, your card/pin or social security number and so on.
TLS has some variations TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2 and now 1.3
- was an upgrade from SSL 3.0 and the difference is significant such that SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 don’t interoperate. Noticeable differences between SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 include but not limited to the following.
- The derivation key function is different.
- TLS has more alerts
1.1 was an upgrade from TLS 1.0 and changes includes but not limited to the following:
- Premature closes no longer cause a session to be non-resumable.
- Implicit Initialization Vector (IV) is replaced with an explicit IV which protect against Cipher block chaining (CBC) attacks.
1.2 was an upgrade from TLS 1.1 and changes includes but not limited to the following:
- Tighter checking of Encrypted Pre-Master Secret version numbers.
- MD5/SHA-1 combination in the pseudorandom function (PRF) was replaced with cipher-suite-specified PRFs.
Now there is TLS 1.3
TLS 1.3 does not support many of the cryptographic algorithms supported by TLS 1.2 which were significant vulnerabilities in TLS 1.2 and this has made TLS 1.3 less vulnerable to attacks.
TLS 1.3 is faster, more secure than TLS 1.2. for example, TLS handshakes in TLS 1.3 only requires one back-and-forth communication instead of two, this shortens the process by some milliseconds for fresh connections and in cases and in cases where the client has already established a prior connection, there will be NO back and forth communication or what we call a round trip. Thus, making the connection faster by some milliseconds which ultimately improves user experience.
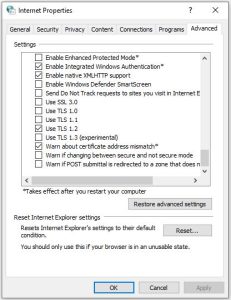
To enable TLS 1.2 protocol on web browsers, see the list below.
- Open Internet Explorer.
- From the menu bar, click Tools > Internet Options > Advanced tab.
- Scroll down to the Security category, manually check the option box for Use TLS 1.2.
- Click OK.
- Close your browser and restart Internet Explorer.
How do I know which version I am using?
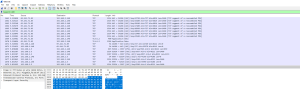
You can use Wireshark to trace your network connection to see the versions of TLS you are using. In the filter, use type tcp.port==443, it will show you the packets that are using SSL security, and identify the versions of TLS as shown below
How to enable using the use of TLS 1.2 /1.3 organization wide using GPO, checkl out this article here


